Finding the profile folder on Windows: Difference between revisions
Dmcritchie (talk | contribs) (Added removal of read-only attributes in profile files) |
Dmcritchie (talk | contribs) m (typo) |
||
| Line 33: | Line 33: | ||
Windows allows you to select a folder and remove the read only attributes for files within the folder and all files within all contained folders. Suggest selecting at least the folder containing the profile folder ('Profiles' folder), | Windows allows you to select a folder and remove the read only attributes for files within the folder and all files within all contained folders. Suggest selecting at least the folder containing the profile folder ('Profiles' folder), | ||
then right-click and select | then right-click and select properties. | ||
First check Read-only files, press Apply button, Apply changes to this folder, subfolders, and files; then redo by unchecking | First check Read-only files, press Apply button, Apply changes to this folder, subfolders, and files; then redo by unchecking | ||
Revision as of 03:31, 26 June 2007
This article will help you find the profile folder for your Mozilla application in Windows 2000 and later. For other operating systems and details about profile folder contents, read Profile folder - Firefox, Profile folder - Thunderbird and Profile folder - SeaMonkey.
The profile folder stores user data for Mozilla applications, such bookmarks, passwords, mail, address books and preference settings and is located separate from the program installation directory. (The installation directory also includes a "profile" folder, for example, C:\Program Files\Mozilla Firefox\defaults\profile, but this folder contains program defaults, not your user profile data.)
When you first install your Mozilla application, a default profile is created. You can later use the Profile Manager to create additional profiles in the same location as the default profile or you can choose a custom location. The default profile folder location is under the C:\Documents and Settings\<Windows login/user name>\Application Data folder in Windows 2000 and XP or under the C:\Users\<Windows login/user name>\AppData\Roaming folder in Windows Vista. These folders are hidden so you need to take special steps to find the profile folder.
Finding your profile
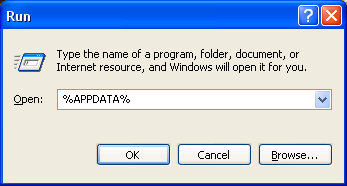
You can use the %APPDATA% variable [1] to quickly find profiles stored in the default location:
Click "Start → Run → Type in %APPDATA% → click OK" (Windows Vista users: Press "Windows key+R" on the keyboard to open the "Run" box; more information here).
This will open a Windows Explorer window showing the contents of the "Application Data" folder in Windows 2000 and XP or the "AppData\Roaming" folder in Windows Vista. You can then open successive folders to get to the profile folder, for example:
- Firefox: Mozilla → Firefox → Profiles
- Thunderbird: Thunderbird → Profiles
- Mozilla Suite or SeaMonkey 1.x: Mozilla → Profiles
You can also specify which folder to open in the "Run" box, for example,
- Nvu: %APPDATA%\Nvu\Profiles
- Sunbird: %APPDATA%\Mozilla\Sunbird\Profiles
You can also use Windows Explorer (or My Computer) to navigate to the profile folder but you will need to enable viewing of hidden files and folders in your Windows Folder Options settings.
From Windows Explorer (or My Computer):
- Windows 2000 and XP: Click "Tools → Folder Options → View (tab) → Show hidden files and folders"
- Windows Vista: Click "Organize → Folder and Search Options → Folder Options → View (tab) → Show hidden files and folders"
You may also wish to deselect the "Hide extensions for known file types" box, if it is checked. Clearing this checkbox will allow you to see the file extensions for all files. Clearing the checkbox for "Hide protected operating system files" might also be required to see hidden files.
Read-only files
Having Read Only Files in your profile folder can cause a lot of problems, including the inability to update bookmarks, cookies, prefs.js and other files. Backing up files to removable media may turn on read-only file attributes by many backup methods, restoring from such media will then result in read-only attributes for the restored files. The XCOPY command will not normally turn on read-only attributes, but copying and moving files with drag and drop usually will turn on read-only file attributes.
Windows allows you to select a folder and remove the read only attributes for files within the folder and all files within all contained folders. Suggest selecting at least the folder containing the profile folder ('Profiles' folder), then right-click and select properties.
First check Read-only files, press Apply button, Apply changes to this folder, subfolders, and files; then redo by unchecking Read-only files, press Apply button, Apply changes to this folder, subfolders, and files; the result will be all files in the profile folders will all have the read-only attribute turned off.
Using Windows Search
You can search for specific files in your profile folder or other hidden locations using Windows Search. In Windows 2000 you must first enable viewing of hidden files and folders, as above.
Windows XP and Vista Search
In Windows XP and Vista, you must enable searching for hidden files and folders in the Search tool itself.
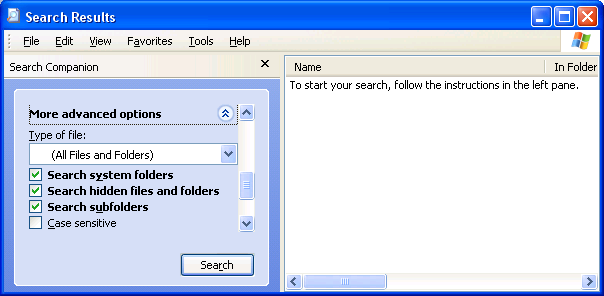
- Windows XP: "Start → Search → More advanced options → select "Search hidden files and folders", as shown above.
- Windows Vista: In the "Advanced Search" area, select "Include non-indexed, hidden, and system files (might be slow)" [2]